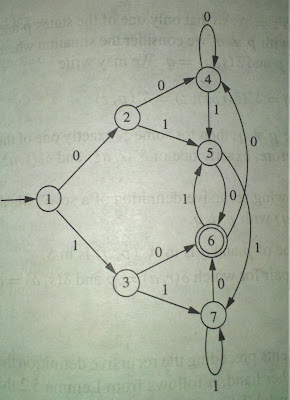
In this given example we have find out the minimization of finite automata with single final state given in the figure below
We can store this FA in a matrix of 2x7 where row represent the input and column represent the states mapped to array_index+1.
State pair can be shown using lower triangular matrix of (number_of_states - 1) x (number_of_states - 1) array as shown in the figure below which can be used to check the equivalent states.
After Minimization the minimized finite automata looks as shown in the figure given below.
Download Source code for c program to minimize the Finite Automata here minimizeFA.c
We can store this FA in a matrix of 2x7 where row represent the input and column represent the states mapped to array_index+1.
State pair can be shown using lower triangular matrix of (number_of_states - 1) x (number_of_states - 1) array as shown in the figure below which can be used to check the equivalent states.
After Minimization the minimized finite automata looks as shown in the figure given below.
Download Source code for c program to minimize the Finite Automata here minimizeFA.c
#include"stdio.h"
#define states 7 //number of states
int
main ()
{
int s1, s2, temp1, temp2, temp3, temp4, i = 0, j =
0, state_pair[states - 1][states - 1], f, k, flag = 1;
int FA[2][states] = { 2, 4, 6, 4, 6, 4, 6, 3, 5, 7, 5, 7, 5, 7 }; //input your state transsion diagram
int xtemp[20], it = 0;
int x[states], l = 0;
int count = 0, arr1[20], arr2[20], c = 0;
int temp[states];
for(i = 0; i < states; i++)
{
temp[i] = 0;
}
for(i = 0; i < states; i++)
{
x[i] = 0;
}
//This is Finite automata for {0,1}*{10}
printf ("\nArray elements are");
for(i = 0; i < 2; i++)
{
printf ("\n");
for(j = 0; j < states; j++)
{
printf ("\t%d", FA[i][j]);
}
}
for(i = 0; i < (states - 1); i++)
{
for(j = 0; j < states - 1; j++)
state_pair[i][j] = 0;
}
printf ("\nEnter final state");
scanf ("%d", &f);
i = f - 2;
j = f - 1;
for(k = 0; k <= f - 2; k++)
state_pair[i][k] = 1;
for(k = 0; k < (states - 1); k++)
{
if(k <= f - 2)
{
}
else
state_pair[k][i + 1] = 1;
}
while(flag)
{
flag = 0;
for(i = 0; i < (states - 1); i++)
{
for(j = 0; j < (states - 1); j++)
{
s1 = i + 2;
s2 = j + 1;
if(s1 > s2)
{
if(state_pair[i][j] != 1)
{
temp1 = FA[0][s1 - 1];
temp2 = FA[0][s2 - 1];
temp3 = FA[1][s1 - 1];
temp4 = FA[1][s2 - 1];
// printf("S1 %d S2 %d\n",s1,s2);
// printf("d(%d,0)=%d \t d(%d,0) %d\n",s1,temp1,s2,temp2);
// printf("d(%d,1)=%d \t d(%d,1) %d\n\n",s1,temp3,s2,temp4);
if(temp1 != temp2) //check whether state p!=q for 0 input
{
if(state_pair[temp1 - 2][temp2 - 1] == 1
|| state_pair[temp2 - 2][temp1 - 1] == 1)
{
state_pair[i][j] = 1;
flag = 1;
}
}
if(temp3 != temp4) //check whether state p!=q for 1 input
{
if(state_pair[temp3 - 2][temp4 - 1] == 1
|| state_pair[temp4 - 2][temp3 - 1] == 1)
{
state_pair[i][j] = 1;
flag = 1;
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
printf ("\nSecond array");
for(i = 0; i < (states - 1); i++)
{
printf ("\n %d", i + 2);
for(j = 0; j < (states - 1); j++)
{
if(i >= j)
{
printf ("\t%d", state_pair[i][j]);
if(state_pair[i][j] == 0)
{
arr1[count] = i + 2;
arr2[count] = j + 1;
count++;
}
}
}
}
printf ("\n\n");
for(i = 0; i < (states - 1); i++)
printf ("\t%d", i + 1);
printf ("\n");
c = 0;
i = 0;
printf ("\n\n");
//code to check the same states(from unmark) start here
while(1)
{
if(x[arr1[c] - 1] == 0 && x[arr2[c] - 1] == 0)
{
x[arr1[c] - 1] = 1;
x[arr2[c] - 1] = 1;
xtemp[it] = arr1[c];
it = it + 1;
xtemp[it] = arr2[c];
it = it + 1;
for(l = 0; l < count; l++)
{
if(x[arr1[l] - 1] == 0 && x[arr2[l] - 1] == 1)
{
x[arr1[l] - 1] = 1;
xtemp[it] = arr1[l];
it = it + 1;
}
if(x[arr1[l] - 1] == 1 && x[arr2[l] - 1] == 0)
{
x[arr2[l] - 1] = 1;
xtemp[it] = arr2[l];
it = it + 1;
}
}
printf("..............following states are in same group...............\n");
for(i = 0; i < it; i++)
printf ("%d\t", xtemp[i]);
it = 0;
}
printf ("\n");
c++;
if(c == count)
break;
}
return 0;
}




0 comments:
Post a Comment